
If a home is to be sold but the record owner is deceased it is imperative to identify who now owns the property. The transaction can then close if the proper parties execute a deed to the buyer.
A formal probate allows for the protection and orderly distribution, after payment of debts, of the assets of the deceased to heirs and/or devisees or a sale to a third party by the personal representative. Nonetheless, even though Washington probates are not expensive or time consuming, they often are not done. But how else will the buyer know that all of the title interest is properly conveyed? What if there are valid liens (including estate taxes or state Medicaid reimbursements) against the estate that would otherwise be paid in probate? That is where the “lack of probate” concept comes into play.
Three Basic Probate Situations
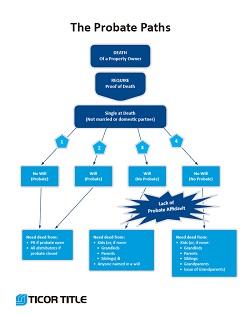
- The owner was single – not married or a domestic partner
- The owner was married or a domestic partner and it was community property
- The owner was married or a domestic partner, but it was separate property (not community property)
There are variations: did the deceased have a will? Is the estate being probated (with or without a will)?
